Table of Contents
If you’re watching a game of cricket, live in person or on TV, it will help to follow play if you understand the various umpire signals. It’s also important for players to know what signals mean, so please read on.
Cricket Umpire Signals
Umpire Signals Quiz
We’ve compiled a quick quiz about umpire signals. Test your knowledge before and after reading this article and see how you have progressed.
1. Out
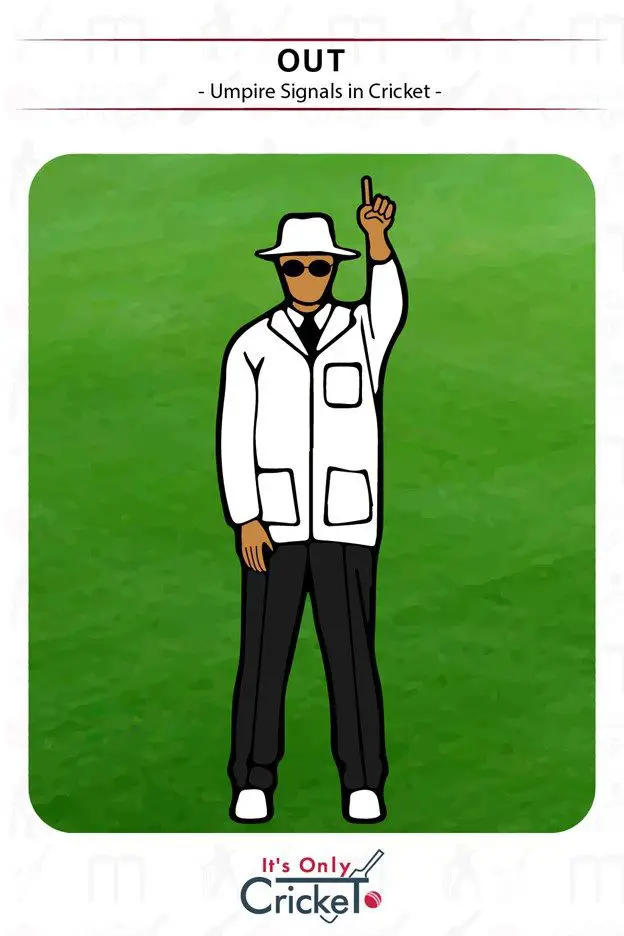

An Out decision means that the umpire has upheld an appeal by the fielding side, and the batsman has been dismissed.
Umpire signal: Raised index finger in the air.
Effect: The batsman is now ‘out’ and must leave the field of play.
2. Not Out
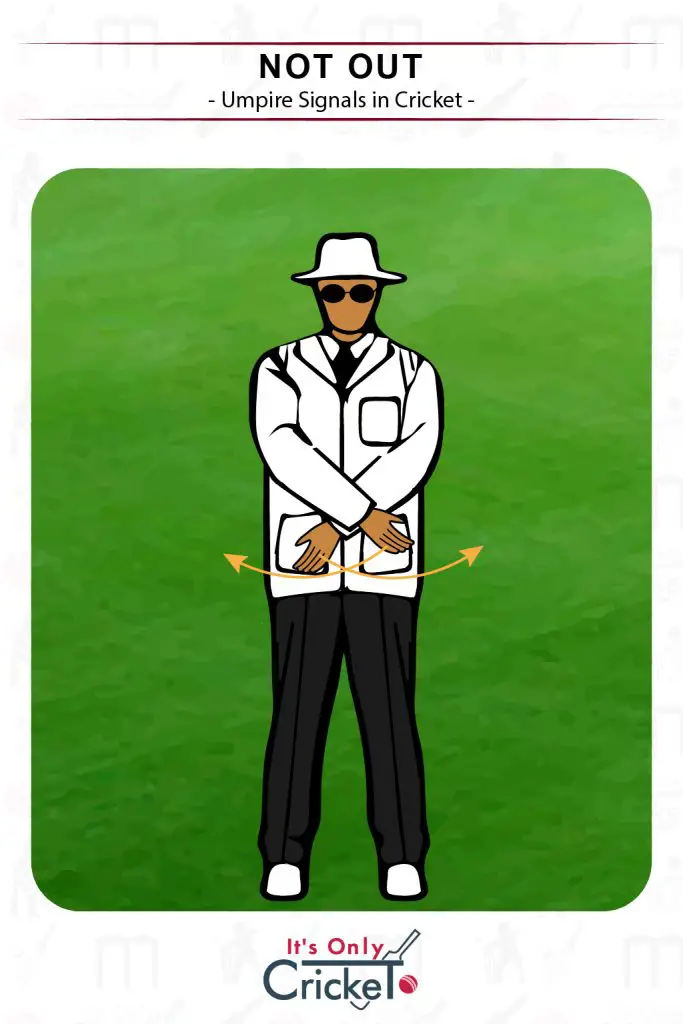

If an ‘out’ decision is successfully overturned on review, the umpire should confirm that the batsman is ‘not out’
Umpire Signal: The signal is made by waving the arms in a sweeping motion out in front of the chest.
Note that if the umpire is turning down an on-field appeal without a referall, they do not have to signal not out. A shake of the head or a call of ‘not out’ is sufficient.
3. No Ball
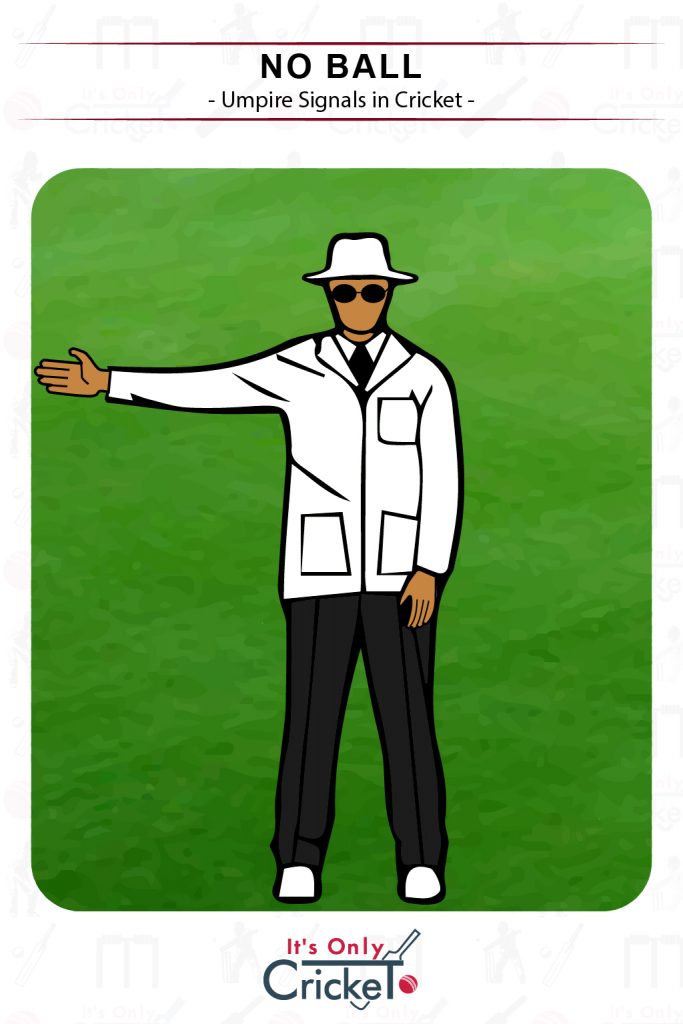

This signal is made when a bowler has sent down an illegal delivery which constitutes a No Ball under the laws.
Umpire Signal: One arm fully extended horizontally.
Effect: One run is added to the batting side’s total (two runs in certain limited overs forms of cricket)
Note that no balls can occur in a number of circumstances including the bowler overstepping or pitching the ball off the cut part of the wicket.
4. Free Hit
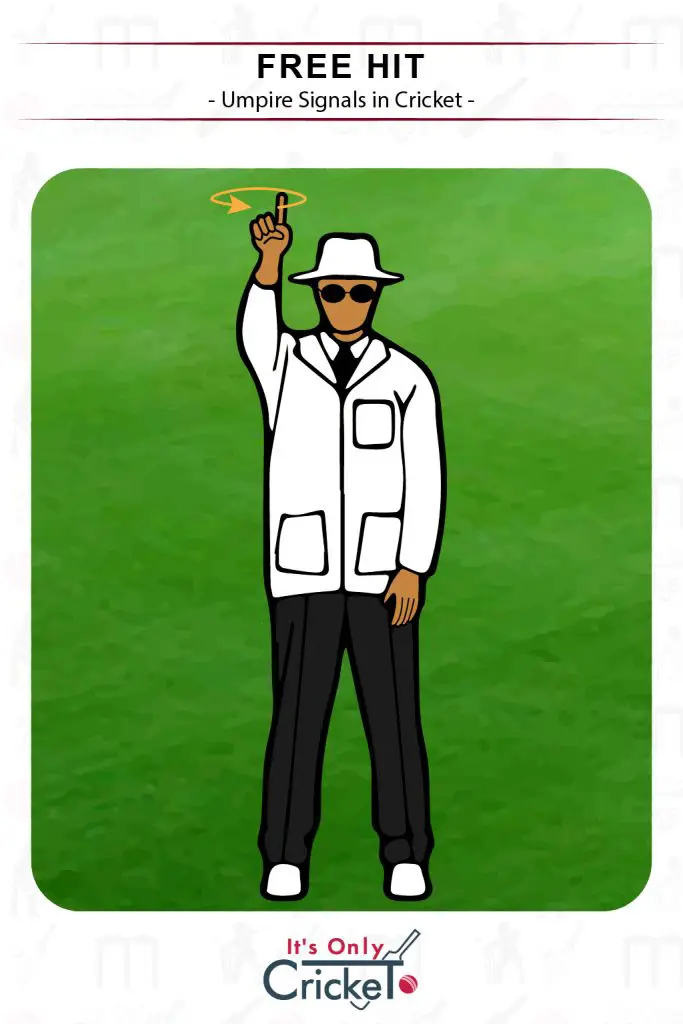

A Free Hit will follow certain types of No Ball deliveries.
Umpire Signal: This is one of the newer umpire signals with one hand held above their head and making a circular motion.
Effect: The batsman can now hit the ball without being dismissed, other than by run out, obstructing the field or hit the ball twice.
5. Wide Ball
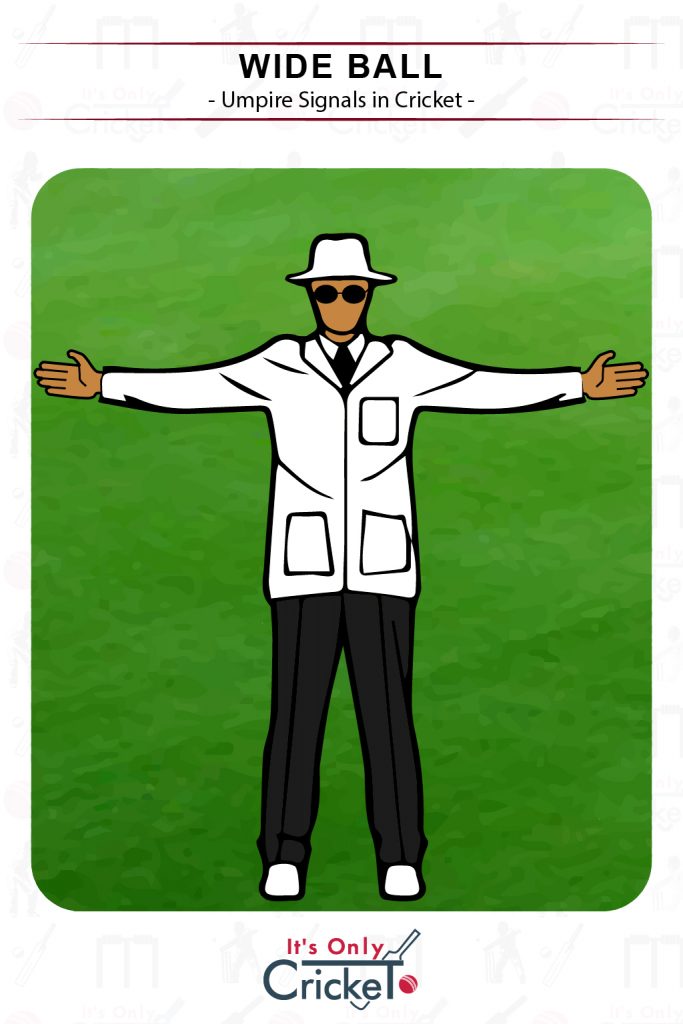

If a wide ball passes the batsman and is deemed to be out of reach when they are standing in their normal stance, the standing umpire should call a wide.
Umpire Signal: Both arms extended horizontally.
Effect: One run will be added to the batting side’s total, and the bowler must deliver that ball again.
Note that wides can also be given based on height.
6. Four Runs
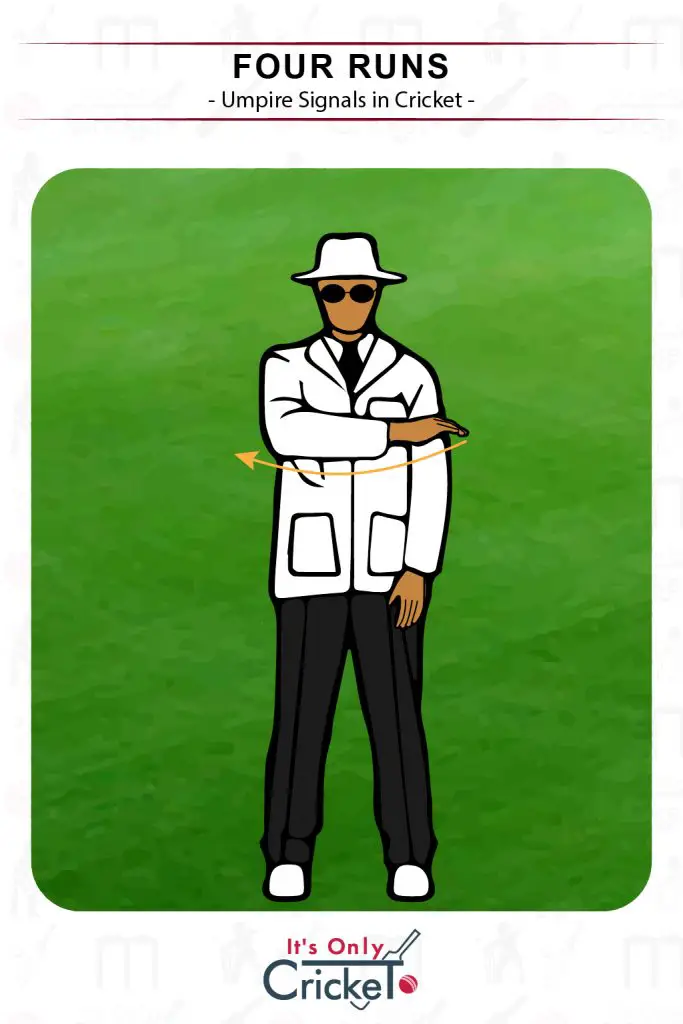

Four runs are signalled when the ball passes the boundary after bouncing at least once.
Umpire Signal: The signal is made by sweeping the right hand across the body three or four times.
Effect: Four runs will be added to the batting side’s total.
If the four runs come as a result of byes, leg byes, no balls or wides, the umpire will make the relevant signal before signalling four runs.
7. Six Runs

Six runs are scored when the batsman hits the ball over the boundary without it bouncing.
Umpire Signal: Both arms held high above the head.
Effect: Six runs are then added to the batting side’s total
8. Bye
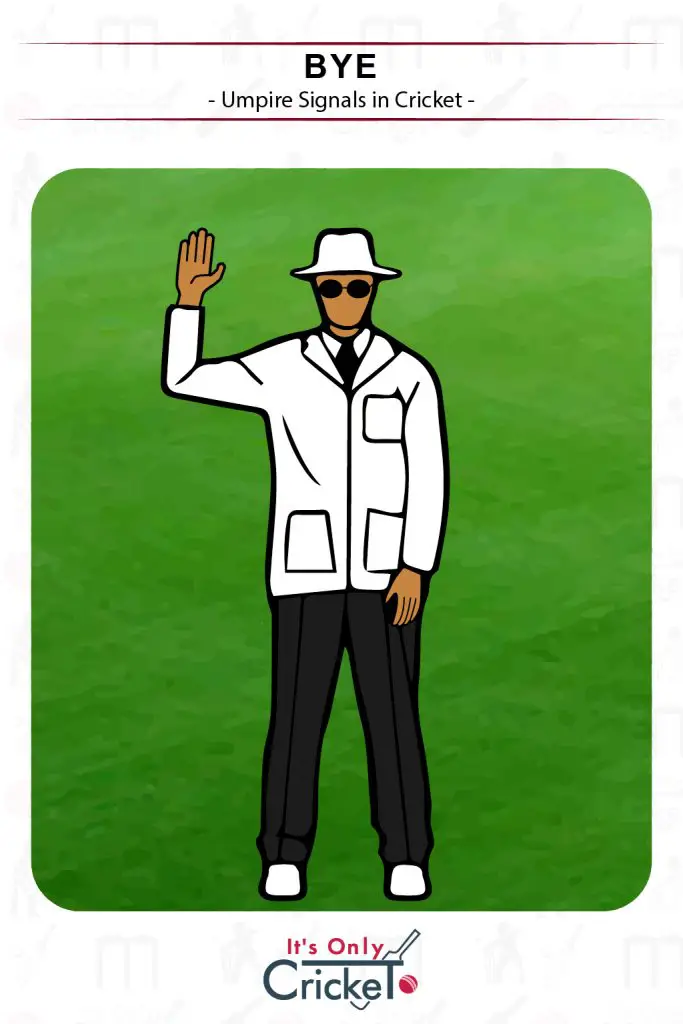

A bye is scored when the ball travels past the stumps and the batsmen are able to run. The ball must not hit the bat or any part of their body.
Umpire Signal: One arm held extended above the head.
Effect: The number of runs completed will be added to the team total
9. Leg Bye
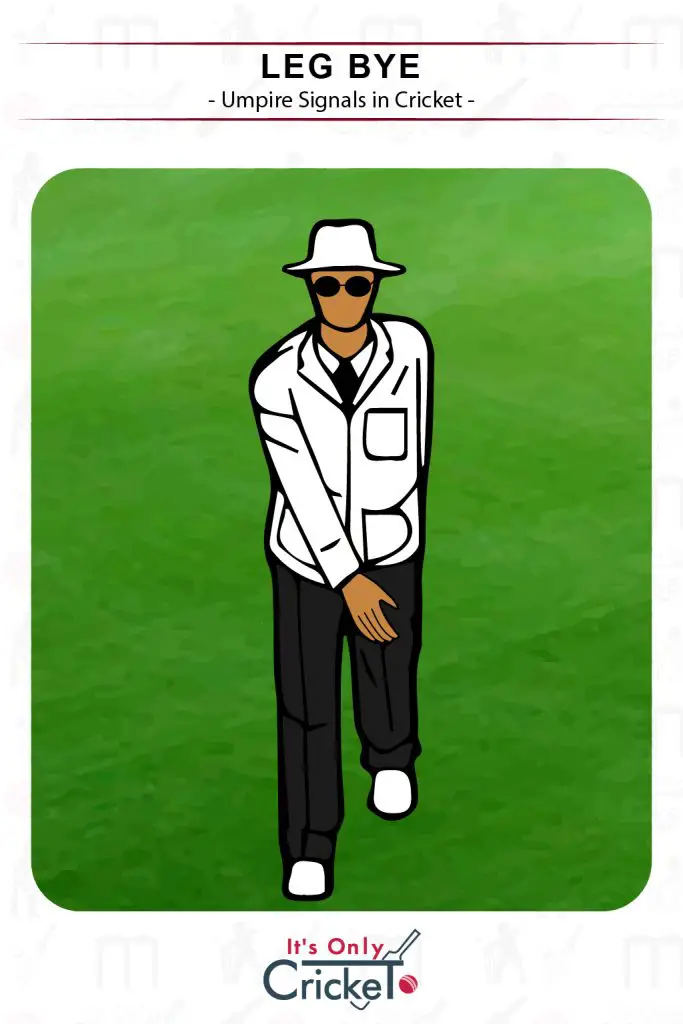

Leg byes are scored when the batsmen run after the ball has hit the batter’s leg or any part of their body, excluding the glove. If the ball hits the glove, then these are counted as runs and are credited to the batter.
Umpire Signal: Raising a knee and tapping it with the hand.
Effect: The number of completed runs is added to the batting team total.
10. Bouncer
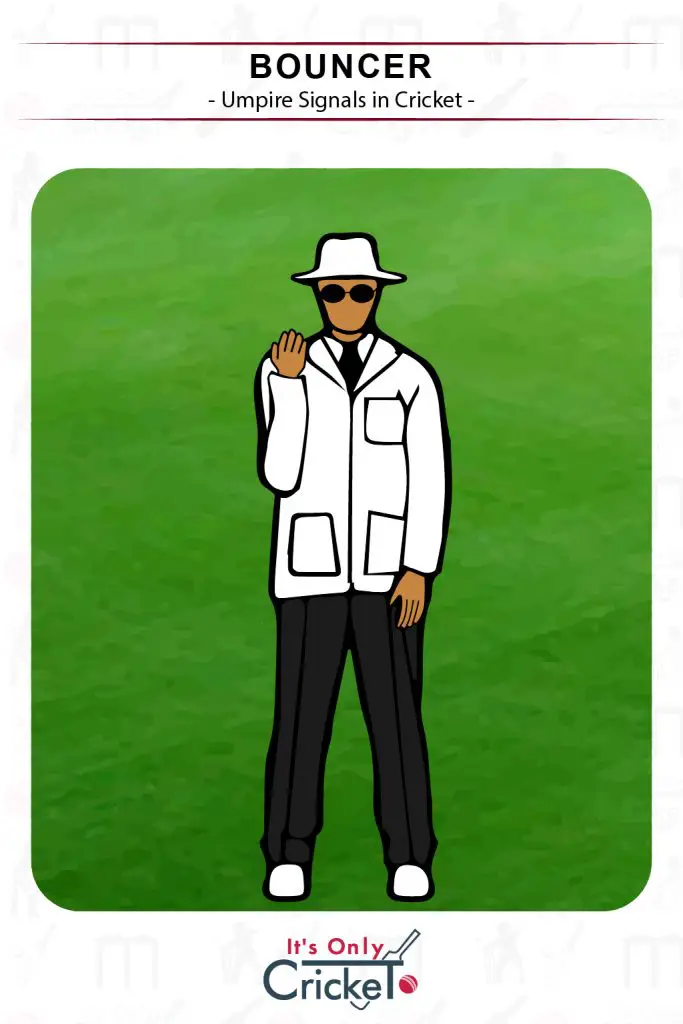

If a ball bounces above shoulder level, the umpire will signal a bouncer.
Umpire Signal: The signal is made by the umpire tapping their right shoulder.
Effect: The bowler and batsmen are made aware that a bouncer has been called and the relevant restrictions on short pitched bowling apply.
11. DRS or Third Umpire
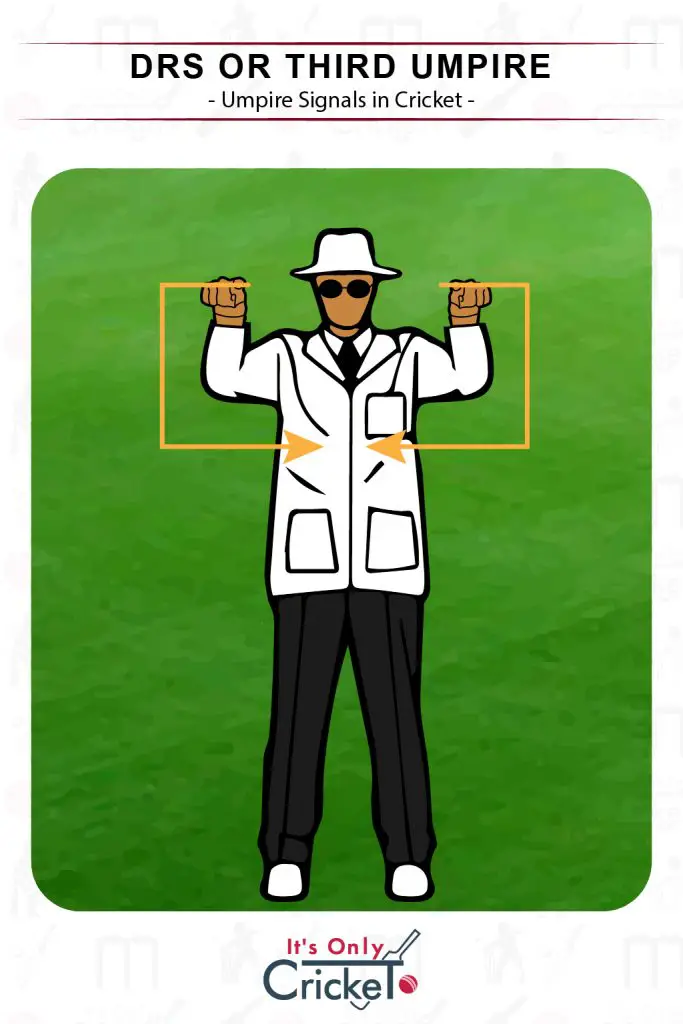
The batting or fielding side can call for the decision review system if they want an on field decision reviewed by the third umpire.
Umpire Signal: Forming a square with the hands.
Effect: The third umpire will review the decision and either uphold or overturn it.
12. Dead Ball
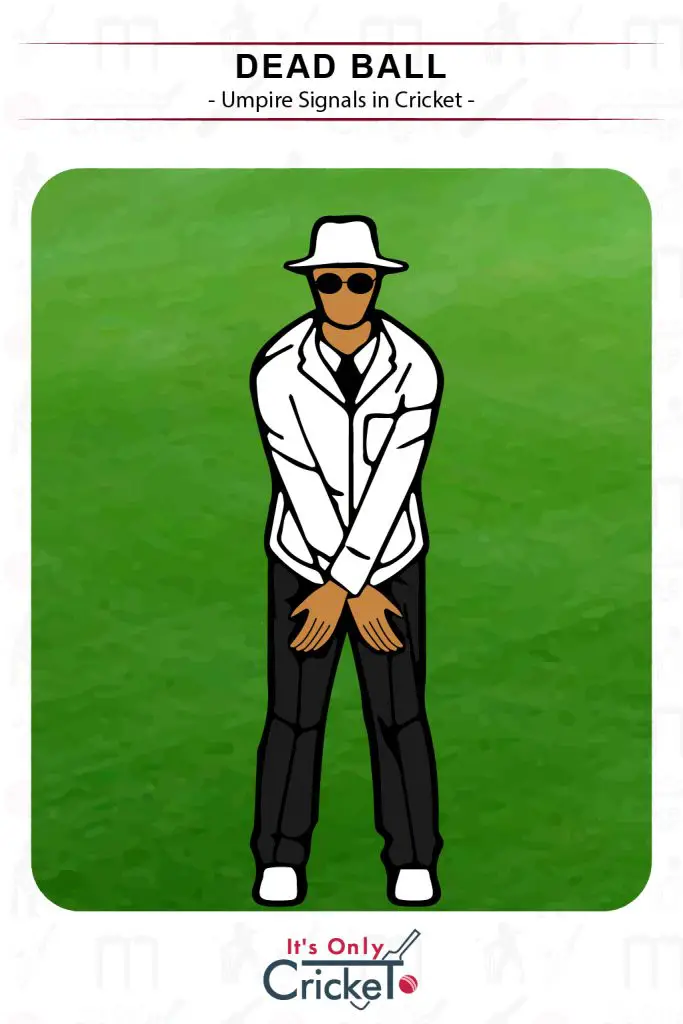

A dead ball can be called in a number of circumstances. Typically, the batter may pull away when the bowler is in their delivery stride.
Umpire Signal: The umpire will sweep both arms across their knees and call ‘dead ball’.
Effect: The dead ball is not counted as a delivery and must be bowled again.
13. Short Run
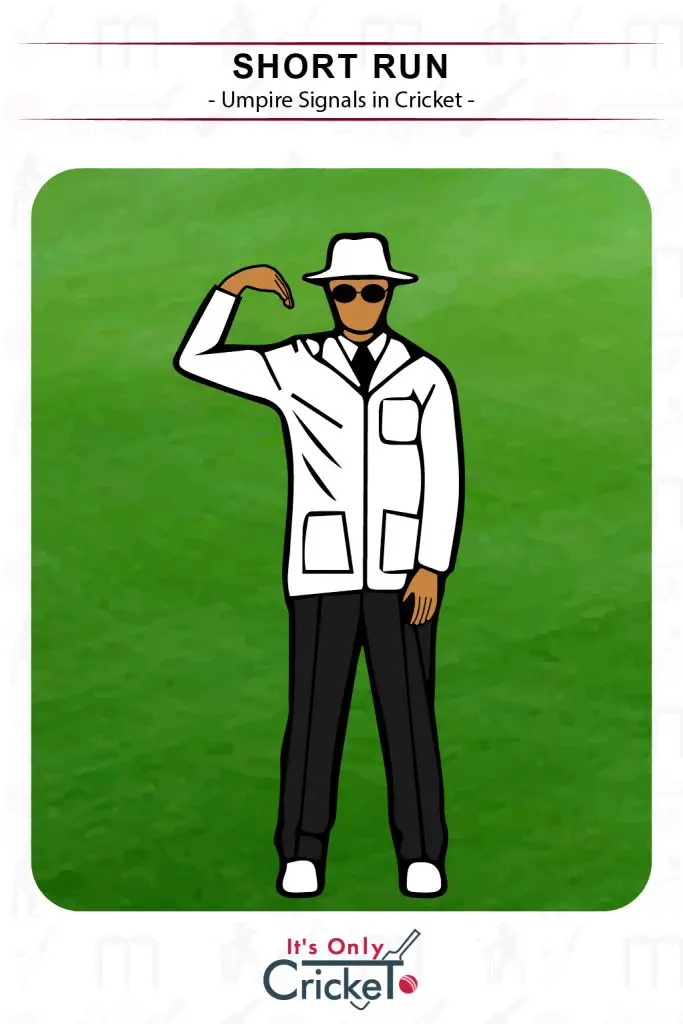

If a batsman fails to ground their bat beyond the popping crease, the umpire should declare a short run.
Umpire Signal: The umpire will tap their shoulder with their arm extended and call ‘one short’
Effect: The incomplete run will not be added to the batting side’s total.
14. Penalty Runs
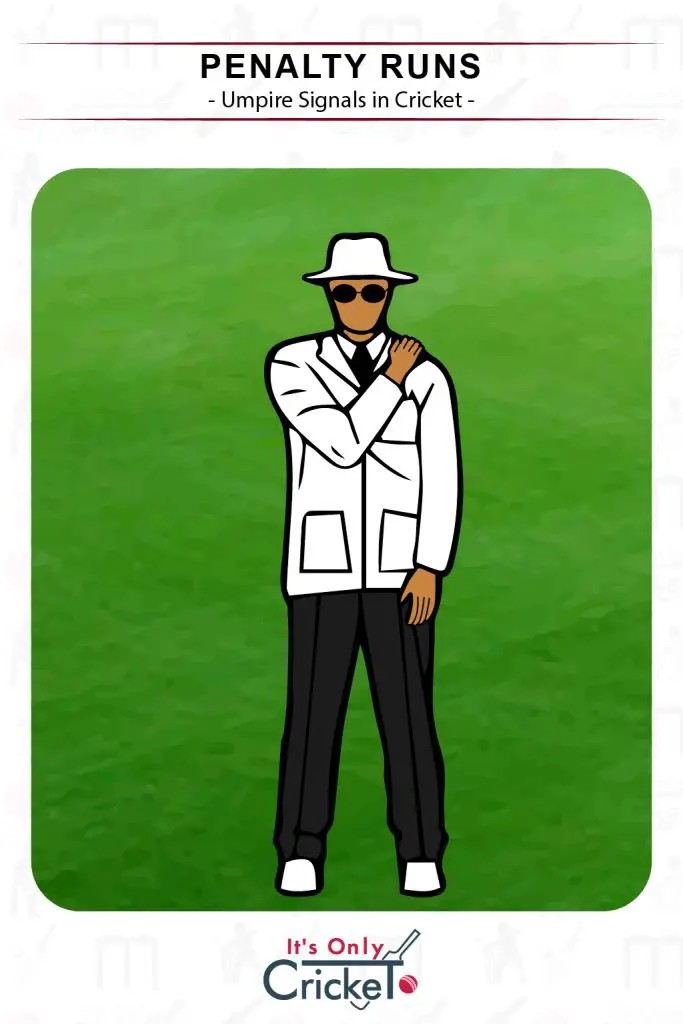

Penalty runs are awarded to batting or bowling sides for a number of different offences.
Umpire Signal: The umpire brings his or her hand across their chest and places it on their shoulder. If they tap their shoulder, runs go to the batting side but, if the hand stays in place, runs go to the fielding side.
Effect: The number of runs, usually 5, will be added to the respective team’s total.
15. Revoke Decision
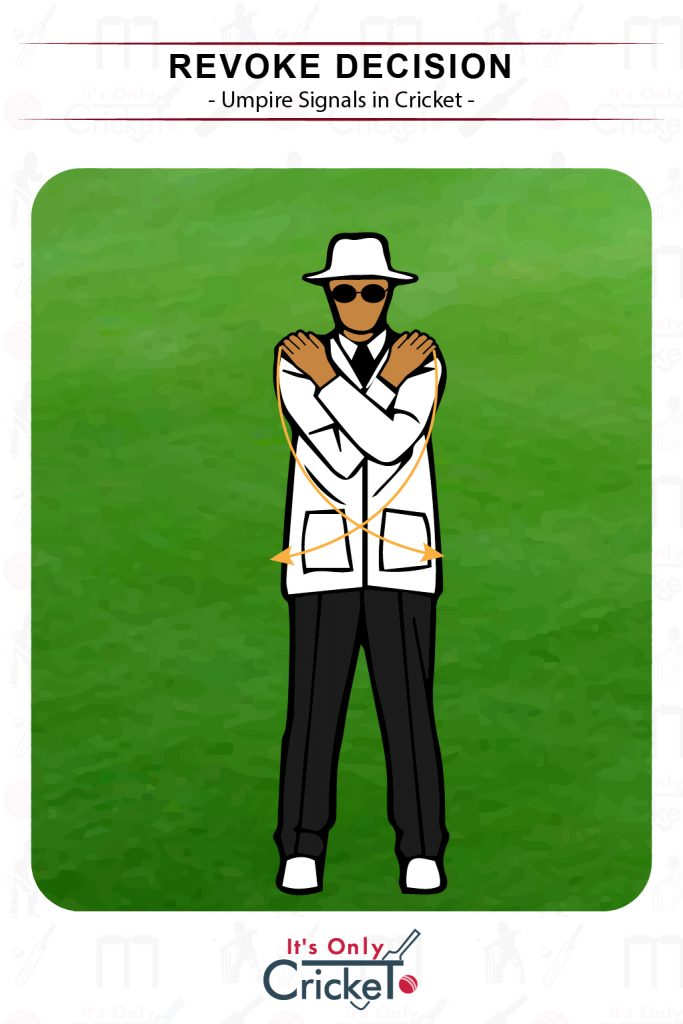

A decision is revoked if it is overturned by the third umpire on review
Umpire Signal: The umpire will cross their arms across their chest and then make a sweeping motion below their waist.
Effect: The original decision is then overturned.
16. Powerplay
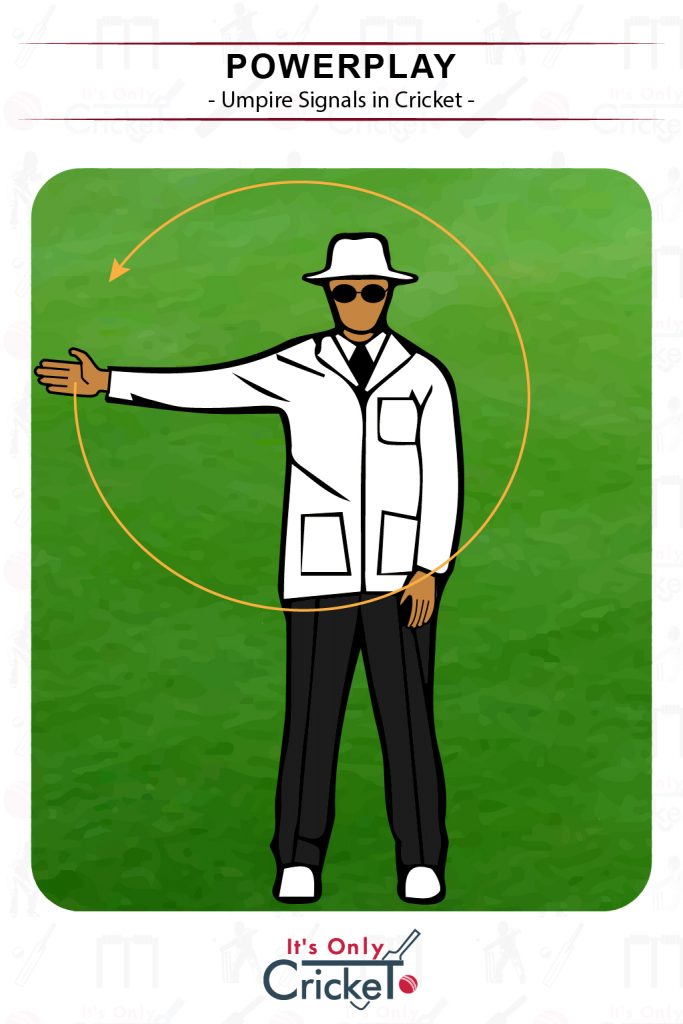
Powerplays apply in limited overs cricket with fielding restrictions in place.
Umpire Signal: The umpire rotates their arm in the air in a ‘windmill’ motion.
Effect: The relevant powerplay will now commence.
17. Soft Signal
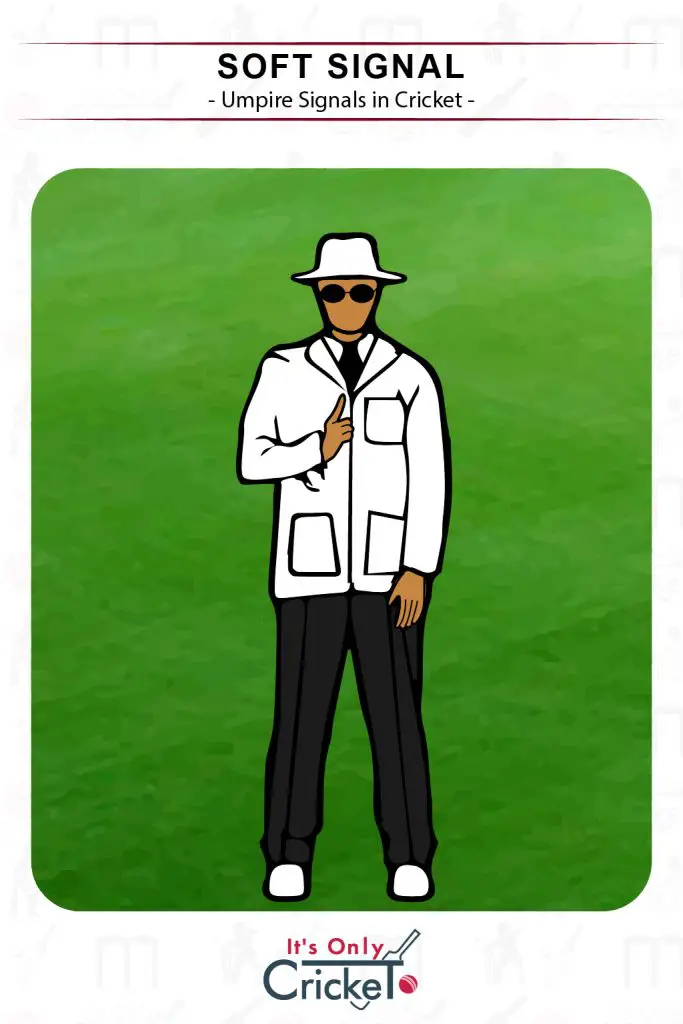

The soft signal is an indication to the third umpire as to what the decision is more likely to be.
Umpire Signal: The umpire will make either the regular out or not out signals.
Effect: The third umpire has to disprove the soft signal beyond doubt or they will uphold it.
18. New Ball
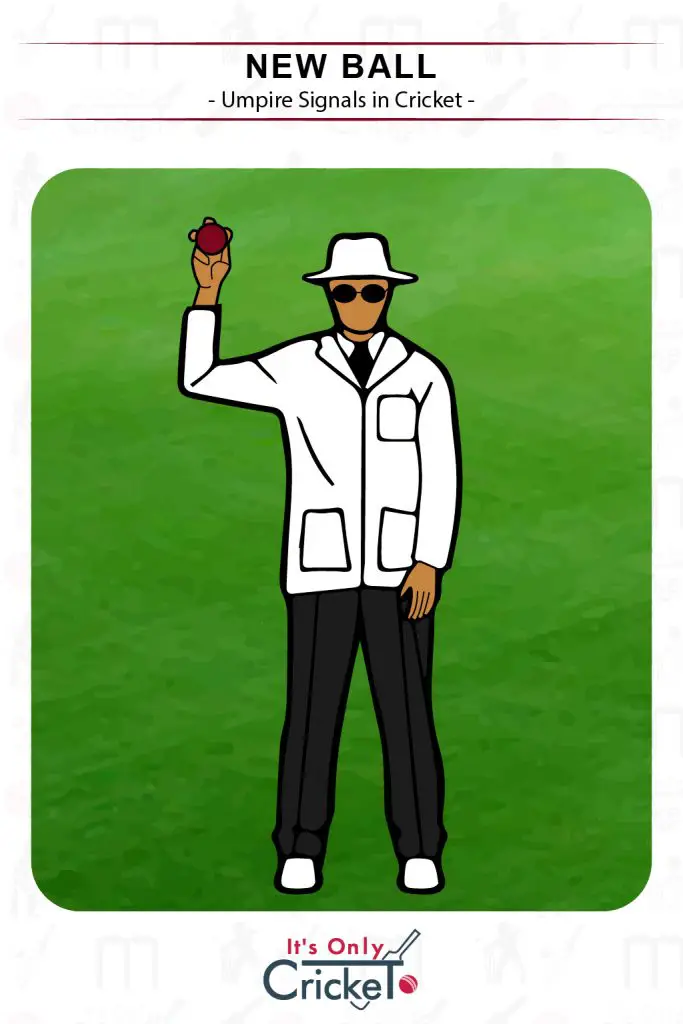

A new ball can be taken after every 80 overs in first class cricket.
Umpire Signal: The umpire holds the new ball in the direction of the scorers.
Effect: The fielding side will now take the new ball.
19. Last Hour
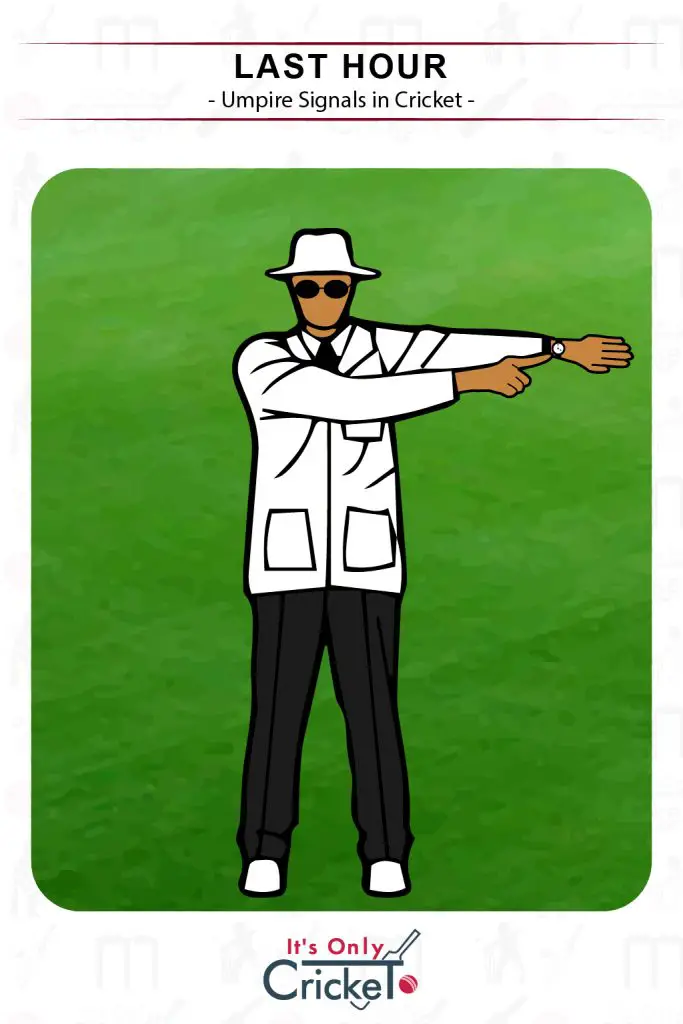

First class cricket has a final hour in place on the last day of the match.
Umpire Signal: Wrist held above the head and pointing to their watch.
Effect: The last hour will now commence.
20. Cancel Call
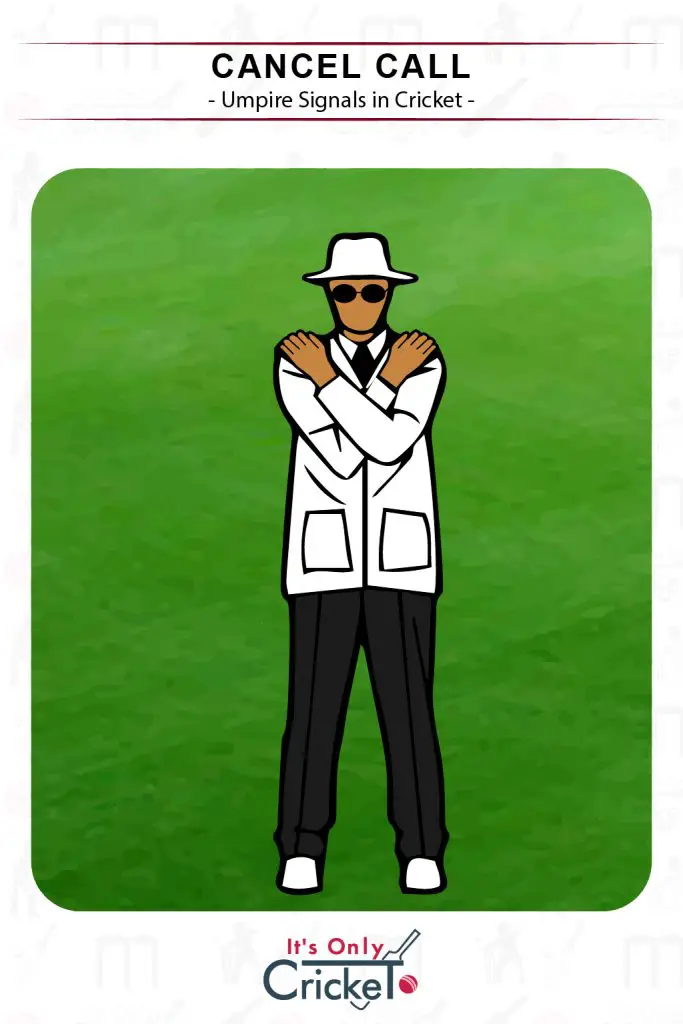

If, for any reason, the umpire has made an incorrect decision, they can use the cancel call signal.
Umpire Signal: Arms crossed and touching the shoulders with the opposite hand.
Effect: The original signal is now cancelled and will no longer stand.
Additions Specific to The Hundred
I wanted to make an addition to this list, but because the signal in question is specific to one tournament, I had to make a separate section. The competition I’m talking about is The Hundred, and one of cricket’s unique hand signals appears here.
Instead of employing overs, this tournament has sets of five balls. At the end of each set, the standing umpire holds a sheet of paper above their head to signify that five legal deliveries have been sent down. It’s one of the oddest cricket signals, but The Hundred is an unusual competition.
Signals in Other Tournaments

Along with The Hundred, there are specific signals for T20 tournaments that won’t appear in other forms of the game. As I write this update in April 2025, the Indian Premier League is in full swing, and there are two additional signals that I see for virtually every game.
The first is for the strategic timeout. This is a break of two minutes and thirty seconds, called by the batting side and the bowling side in each innings. The umpire makes the signal for this timeout by raising their hand in the air and tapping their watch.
The second signal that I wanted to mention was the one for the impact sub. At any stage in the game, a team can withdraw a player and replace them. The rules are quite complicated, but the important point here is the signal. The umpire raises both hands above their head and crosses their arms. I haven’t included these signals in the quiz, as you won’t see them in test cricket, but it’s worth mentioning them as the IPL is such a popular tournament, and it helps to know what they mean.
Does the Square Leg Umpire Make Any Signals?

The umpire standing at square leg may be called upon to make a signal. Usually, this will be in the case of a run out or stumping appeal at the batter’s end. If the square leg umpire is happy that the batter is out of their ground, they will raise their finger to confirm that the batter is out.
If the umpire is unsure about the decision, they will make the signal which refers the matter to DRS.
The square leg umpire can also assist the umpire at the bowling end by making soft signals. Usually, these will apply in limited overs matches. For example, if a ball is over head height, they can make the wide or no ball signal. Similarly, if a ball is delivered at above waist height without bouncing, the no ball signal is made once again.
Does the Third Umpire Make Any Signals?
No, the third umpire does not need to make any hand signals during their duties off the field. They will, however, need to make decisions on run outs and stumpings that will need to be conveyed to the spectators via the big screen.
Based on the umpire’s decision, technicians will press a button that states whether the batter is out or not out.
You could argue that this is one of the legitimate umpire signals in cricket, but it isn’t made on the field of play.
Closing Thoughts
Having read through these signals, you should now be able to have a greater understanding of cricket. Who knows, you may even take that knowledge a stage further and become a local umpire yourself.


