Table of Contents
I’ve often wondered about how they measure distance hitting in cricket. If you’re also in the dark, then please read on and I’ll look to explain it.
Six Hitting Distances
At the big tournaments such as the Indian Premier League, we often see a six distance come up almost as soon as the ball comes to rest. The confusion for me lies in the fact that that ball will often hit seating in the stand or some other part of the building, so how do they know how far the ball would have travelled before it hit the ground?.
If it lands on the stadium roof, that would also disrupt its final landing point. Even if the ball travels cleanly and lands on the ground without any interference, just how is that measured?
The answer lies in the Hawkeye technology that is seen in other areas of cricket.
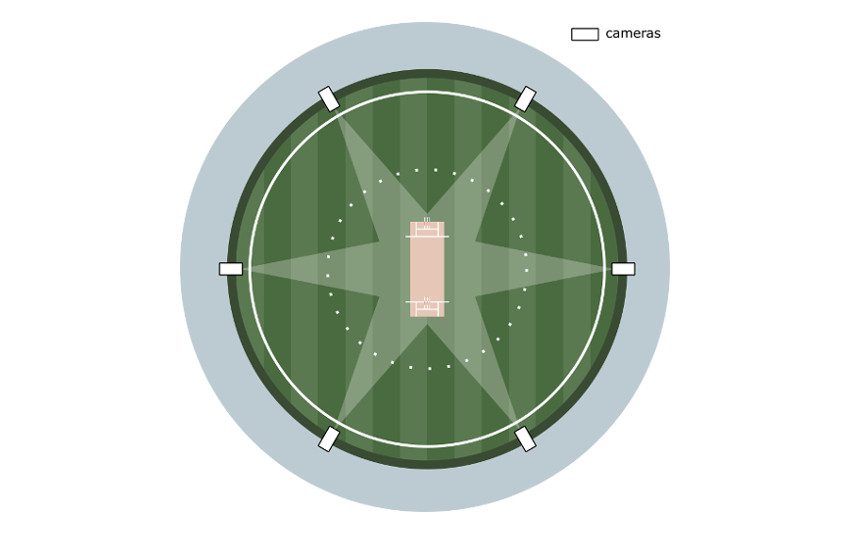
How is a Six Measured in Cricket?
In every game where technology is used, Hawkeye is involved. They have six cameras strategically placed around the ground and these are used to monitor the flight of the ball as it travels away from the batter’s bat.
Those six cameras then combined to form a 3D image of the ball’s trajectory. That image will then help to gauge the final distance and where the ball would land.
Speed is naturally important too. The speed is calculated from the moment the ball leaves the bat. The time it takes to travel 22 yards (the length of a cricket pitch) is also recorded and this is projected forward.
Using calculations involving that 3D Image plus the trajectory and speed of the ball, the final distance is then determined.
Alternative Methods
A radar gun, similar to that which is used to measure bowling speeds, can also be used in this process. In terms of six hitting, it will calculate the speed of the ball as it leaves the bat and travels across the cricket field.
The gun is often used in games where Hawkeye isn’t available. When this happens, the measuring applies a law of physics which is known as the Range of Projectile.
As you might have imagined, range of projectile can be used in missile technology where it’s essential to know how far something can travel, but it can also be applied to six hitting in cricket. The calculations involved can be quite complex.
Essentially, the physics uses the speed of the ball, its trajectory and the time that it stays in the air. A system of divisions and calculations is then employed to get a final answer.
How Accurate is the Technology?
As with many areas of cricket technology, the systems used to calculate six hitting are not 100% perfect. In terms of the Range of Projectile Calculations, there is a problem in the sense that it uses the time that the ball stays in the air.
As we’ve seen, there are potential issues with this. That ball, for example, can connect with a part of the stand while it is still travelling in an upwards direction.
With the Hawkeye method, speed is measured but any drops in that speed, for whatever reason, can be variable. However, the margins of error are small ones, and the technology is certainly much better than it would have been in the past.
Why is Measuring Distance Important?
Naturally, a big part of this is down to entertainment. The crowd love to see big sixes, particularly in the shorter formats where the bat dominates the ball. When a six extends beyond 100 metres, the crowd goes wild and the commentators get pretty excited too.
It may also be useful to monitor whether there are more 100+ metre sixes in the game. Cricket could eventually get to the same point as golf, where the courses just aren’t big enough for the power hitters of the modern day. It could also be an issue with equipment where heavier and bigger bats continue to give the batsmen the edge.
There’s not much that can be done about this factor: Organisers are restricted by the grounds that are already in place, but they could look to push boundaries back as far as they possibly can. In time, bigger stadiums could be built, but that simply isn’t feasible in countries where cricket doesn’t generate huge revenue.
Batters and coaches would also use stats relating to the biggest sixes in the game. It’s a sign of who is in form, and the figures would have some influence at the IPL and other franchise auctions.
For now, it’s all about another fun element, but there are some serious reasons for measuring six hits in cricket.
The Biggest Sixes in Cricket
My interest in this subject increased when I saw Liam Livingstone hit a monster six for Punjab Kings at the IPL in 2022. It was measured at 117 metres but it had hit the stadium roof so how did they know this was accurate?
Hopefully we’ve now cleared that up. If you’re interested, I have also written an article on the biggest sixes in the game. Livingstone is a power batter with a long range but he has plenty of competition from the past and in the modern day.


